Don't miss our holiday offer - up to 50% OFF! ? | Follow Our Social : ![]()
![]()
Tinnitus: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & Natural Relief Options
Tinnitus is a common hearing condition where a person hears ringing, buzzing, hissing, humming, or clicking sounds in the ears without any external sound source. Often described as “ringing in the ears,” tinnitus can be temporary or chronic and may affect one or both ears. Millions of people worldwide search daily for answers about tinnitus causes, tinnitus treatment, how to stop ringing in the ears, tinnitus relief, and natural remedies for tinnitus. Although tinnitus is not a disease itself, it is usually a symptom of an underlying issue related to hearing health, nerve function, blood circulation, or ear conditions. Understanding what causes tinnitus and how to manage it is the first step toward long-term relief.
What Is Tinnitus?

How Tinnitus Happens
Tinnitus usually occurs when there is a problem somewhere along the hearing pathway. This includes:
The inner ear (cochlea)
The auditory nerve
The brain’s sound-processing centers
When the brain does not receive normal signals from the ears (for example, due to hearing loss), it may “create” sound to fill the gap. This is one of the main reasons tinnitus is often linked to hearing damage.
Is Tinnitus Common?
Yes, tinnitus is very common. Millions of people worldwide experience tinnitus, and it affects both men and women. It is more common in:
Adults over 40
People exposed to loud noise
Musicians, factory workers, construction workers
Military personnel and veterans
People with hearing loss
Because of this, tinnitus is one of the most searched hearing conditions online.
Types of Tinnitus
1. Subjective Tinnitus
This is the most common type. Only the person affected can hear the sound. It is usually caused by hearing loss, nerve damage, or inner ear problems.
2. Objective Tinnitus
This is rare. A doctor may be able to hear the sound during an examination. It is often linked to blood vessel problems, muscle contractions, or structural issues in the ear.
What Does Tinnitus Sound Like?

Tinnitus does not sound the same for everyone. Common descriptions include:
Ringing
Buzzing
Hissing
Clicking
Whistling
Roaring
Pulsing (heartbeat-like sound)
Some people hear a high-pitched tone, while others hear a low rumbling noise. The sound may be constant or come and go.
Is Tinnitus Dangerous?
Tinnitus itself is not usually life-threatening, but it should never be ignored because it can be a sign of an underlying health problem such as hearing loss, circulatory disorders, ear infections, nerve damage, high blood pressure, or even neurological conditions. While the ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds may not directly cause physical harm, untreated tinnitus can seriously affect quality of life, leading to chronic stress, anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, poor concentration, and emotional exhaustion. In some cases, tinnitus may signal more serious issues like acoustic neuroma, Meniere’s disease, or vascular problems, especially if it appears suddenly, occurs in only one ear, or is accompanied by dizziness, hearing loss, or balance problems. For this reason, tinnitus should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out serious causes and to begin proper management early, helping to prevent long-term complications and worsening symptoms.
Can Tinnitus Go Away on Its Own?
Yes, tinnitus can go away on its own in some cases, especially when it is caused by temporary factors such as loud noise exposure, earwax buildup, minor ear infections, sinus congestion, stress, or short-term medication side effects. This type of tinnitus is known as temporary or acute tinnitus, and it often resolves once the underlying trigger is removed or treated. For example, ringing in the ears after attending a loud concert may fade within hours or days as the ear recovers, and tinnitus caused by earwax blockage may disappear after proper cleaning. Similarly, tinnitus linked to colds, flu, or sinus infections may improve as inflammation and fluid clear from the ear. However, when tinnitus is caused by permanent hearing damage, nerve injury, aging, long-term noise exposure, circulatory disorders, or chronic medical conditions, it is less likely to go away completely on its own and may become chronic tinnitus. In such cases, while the sound may not disappear entirely, many people experience significant improvement with proper treatment, sound therapy, lifestyle changes, stress management, and nutritional support. It is also important to note that the brain can adapt over time through a process called habituation, where tinnitus becomes less noticeable even if it is still present. Because it is impossible to know whether tinnitus will resolve on its own without evaluation, anyone experiencing persistent, worsening, or sudden tinnitus should seek medical advice to identify the cause and prevent potential long-term complications.
Why Understanding Tinnitus Matters
Understanding tinnitus is extremely important because it empowers individuals to recognize early warning signs, seek timely medical evaluation, and take the right steps toward effective management before the condition worsens. Many people ignore ringing in the ears, assuming it will go away, but tinnitus can be an early indicator of hearing damage, nerve problems, circulatory issues, or underlying medical conditions that require attention. When people understand what tinnitus is, what causes it, and how it affects the brain and auditory system, they are better equipped to avoid triggers such as loud noise exposure, ototoxic medications, and chronic stress, all of which can worsen symptoms. Proper knowledge also reduces fear and anxiety, helping sufferers feel more in control and motivated to explore treatment options, lifestyle changes, and natural remedies. Ultimately, understanding tinnitus leads to earlier diagnosis, better treatment outcomes, improved quality of life, and long-term hearing protection, making it a critical part of maintaining overall health and well-being.
Here are some tinnitus relief products and natural supplement options sold on Amazon.com that many people explore for support with ringing in the ears, buzzing symptoms, or auditory wellness — though individual results vary and clinical support may be limited:







🧠 What to Know Before Buying
Many of these are supplement-based products or topical aids, not medical cures.
Ingredients like ginkgo biloba are frequently chosen for their antioxidant and circulation-supporting effects.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements, especially if you’re taking medications, pregnant, nursing, or have health conditions.
🌿 Natural & Supplement Options
XPRS Nutra Organic Ginkgo Biloba Powder – Ginkgo biloba extract is one of the more commonly used natural ingredients for tinnitus relief because it may help support circulation and nerve health, which in some people can reduce the perception of ringing.
Luhaka Tinnidrop Tinnitus Relief Spray – A topical ear spray marketed for soothing ear sensations; some people use it alongside other strategies for symptom management.
💊 OTC & Targeted Formulas
Cleartone Tinnitus Treatment Capsule – Dietary capsule aimed at temporarily calming or easing tinnitus sounds, though scientific support is limited compared with medical treatments.
Phytage Labs Tinnitus 911 Tinnitus Relief Supplement – A tinnitus supplement blend with mixed reviews, intended to support ear ringing relief. As with all supplements, effectiveness can vary by person.
Common Causes of Tinnitus

Tinnitus is not a disease but a symptom of an underlying problem, and understanding its causes is key to finding effective treatment. Millions of people search for terms like tinnitus causes, why do my ears ring, and what causes ringing in the ears, which shows how important this topic is for those affected.
Tinnitus can arise from a wide range of factors, including hearing loss, exposure to loud noise, circulatory issues, medications, or even stress. While the exact cause varies from person to person, some causes are more common than others.
1. Hearing Loss
Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis) and noise-induced hearing loss are among the most common causes of tinnitus. When hair cells in the inner ear are damaged, the brain receives incomplete auditory signals, often creating phantom sounds such as ringing or buzzing.
2. Exposure to Loud Noise
Extended exposure to loud environments—like concerts, construction sites, industrial machinery, or even prolonged headphone use—can trigger tinnitus. This type of tinnitus may be temporary initially but can become chronic with repeated exposure.
3. Earwax Blockage
Excessive earwax can irritate the eardrum or block the ear canal, leading to pressure changes and tinnitus. Removing the blockage often resolves the symptoms.
4. Ear Infections or Fluid in the Ear
Middle or inner ear infections, as well as fluid accumulation due to colds or sinus infections, can disrupt hearing and create a buzzing or ringing sound.
5. Head or Neck Injuries
Trauma to the head, neck, or jaw can affect the auditory nerves, inner ear structures, or blood flow, resulting in tinnitus. These cases often require medical evaluation to prevent long-term complications.
6. Medications
Certain medications, known as ototoxic drugs, can trigger tinnitus as a side effect. These include:
Some antibiotics (e.g., gentamicin)
Chemotherapy drugs
High doses of aspirin
Loop diuretics
7. Circulatory or Cardiovascular Problems
Tinnitus can sometimes be caused by blood flow issues, such as high blood pressure, atherosclerosis (narrowed arteries), or turbulent blood flow near the ear. This can create a pulsating sound that matches the heartbeat, known as pulsatile tinnitus.
8. Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
Problems with the jaw joint can affect surrounding nerves and muscles, leading to tinnitus. TMJ-related tinnitus may be accompanied by jaw pain, clicking, or difficulty chewing.
9. Stress and Anxiety
Chronic stress, anxiety, and tension can worsen tinnitus or even trigger it in susceptible individuals. Stress increases cortisol levels, which may amplify the brain’s perception of internal sounds.
10. Other Causes
Meniere’s disease – a disorder of the inner ear causing tinnitus, vertigo, and hearing loss
Acoustic neuroma – a benign tumor on the auditory nerve
Thyroid problems – affecting metabolism and circulation
Tinnitus can result from hearing loss, loud noise exposure, ear infections, medications, circulatory problems, or stress. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment and symptom relief. Early evaluation by an ENT doctor, audiologist, or primary care physician can help prevent worsening and improve quality of life.
Symptoms of Tinnitus
Tinnitus is often described as a ringing in the ears, but it can manifest in a variety of sounds and severities. Understanding the symptoms is critical for early detection, proper evaluation, and effective management. Millions of people search for terms like tinnitus symptoms, ringing in ears at night, and buzzing sound in ears, reflecting how widespread and concerning these symptoms are. Tinnitus is not always the same for everyone. Symptoms can vary in type, intensity, duration, and timing, depending on the underlying cause.
Common Sounds Associated with Tinnitus
People with tinnitus may experience:
Ringing – high-pitched or low-pitched continuous sound
Buzzing – similar to the hum of a machine or appliance
Hissing – soft or loud static-like noise
Clicking – rhythmic or irregular clicking sounds
Whistling or Roaring – sounds resembling ocean waves or wind
Pulsing – a heartbeat-like sound, known as pulsatile tinnitus
Search-friendly phrases: ringing in the ears, buzzing in ear, hissing sound in ears, pulsating tinnitus
Other Physical and Sensory Symptoms
In addition to auditory sensations, tinnitus may be accompanied by:
Hearing changes – mild hearing loss or difficulty following conversations
Ear fullness – feeling of pressure in one or both ears
Ear pain or discomfort – especially if linked to infection or injury
Dizziness or balance issues – common in inner ear-related tinnitus
Emotional and Cognitive Effects
Tinnitus can affect mental health and daily functioning:
Difficulty concentrating – the constant sound can interfere with focus
Sleep disturbances – tinnitus often worsens at night when the environment is quiet
Irritability or anxiety – persistent noise may cause stress and frustration
Depression or mood changes – in severe chronic cases
Patterns and Timing of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can occur:
Constantly – a persistent sound throughout the day
Intermittently – comes and goes without warning
Unilateral – in one ear only
Bilateral – in both ears
Some people notice tinnitus only in quiet environments or when under stress, making it more noticeable at night or during work requiring focus.
When Symptoms Require Urgent Attention
Seek immediate medical care if tinnitus is accompanied by:
Sudden hearing loss
Severe dizziness or vertigo
Ear pain or discharge
Pulsating sounds in sync with heartbeat
Neurological symptoms such as weakness or facial numbness
Tinnitus symptoms are diverse and affect both hearing and overall quality of life. Common symptoms include ringing, buzzing, hissing, or pulsating sounds, sometimes accompanied by hearing loss, dizziness, or emotional distress. Recognizing these symptoms early and consulting a healthcare professional can significantly improve management and reduce impact on daily life.
Is There a Cure for Tinnitus?
Tinnitus, commonly described as ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the ears, affects millions of people worldwide. A frequent question among sufferers is: “Is there a cure for tinnitus?” The short answer is: there is currently no universal cure, but there are highly effective ways to manage, reduce, or control tinnitus symptoms, depending on the underlying cause. Millions of people search for phrases like tinnitus cure, how to stop ringing in ears permanently, natural tinnitus remedies, and best treatment for tinnitus, highlighting the widespread concern and demand for effective solutions.
Why Tinnitus Is Hard to Cure
Tinnitus is not a disease itself; it is a symptom caused by a variety of conditions, including:
Hearing loss (age-related or noise-induced)
Ear infections or wax buildup
Circulatory or blood flow problems
TMJ (jaw joint) disorders
Neurological issues
Side effects of certain medications
Because the causes are so diverse, there is no single treatment that works for everyone. Successful tinnitus management often requires a combination of therapies tailored to the individual.
Medical Treatments and Interventions
While a universal cure is not yet available, several treatments can significantly reduce tinnitus symptoms:
Hearing Aids – For those with hearing loss, improving auditory input can decrease the perception of tinnitus.
Sound Therapy – Using white noise machines, nature sounds, or tinnitus maskers can reduce the impact of ringing.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – Helps patients cope with tinnitus-related stress, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
Medication Adjustments – If tinnitus is caused by ototoxic drugs, a doctor may modify prescriptions.
Surgery or Medical Intervention – Rarely, structural issues like vascular problems or tumors may require surgical treatment.
Natural and Home Remedies
Many people also seek natural remedies for tinnitus as part of a holistic approach:
Supplements: Magnesium, Vitamin B12, Ginkgo biloba, and Zinc may support nerve and ear health.
Dietary changes: Reducing caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods while eating anti-inflammatory foods can help.
Stress management: Meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises often improve symptom perception.
Noise control: Avoiding loud sounds and using ear protection can prevent worsening of tinnitus.
Can Tinnitus Go Away on Its Own?
In some cases, tinnitus is temporary:
After loud noise exposure (concerts, machinery)
Following earwax removal or treatment of an infection
Due to transient circulatory changes or medication side effects
However, chronic tinnitus may require long-term management. Early intervention, proper diagnosis, and a combination of medical and lifestyle strategies often result in the most noticeable relief. While there is no guaranteed cure for tinnitus, the condition can be managed effectively through a combination of medical treatment, sound therapy, lifestyle adjustments, cognitive behavioral therapy, and natural remedies. Understanding the cause of tinnitus is crucial, and early intervention improves the chances of reducing its impact. Millions of people benefit from tinnitus management programs, which focus on both symptom relief and improving quality of life. Using this comprehensive approach, tinnitus sufferers can regain control over their hearing and daily comfort.
Best Tinnitus Treatments & Management Options
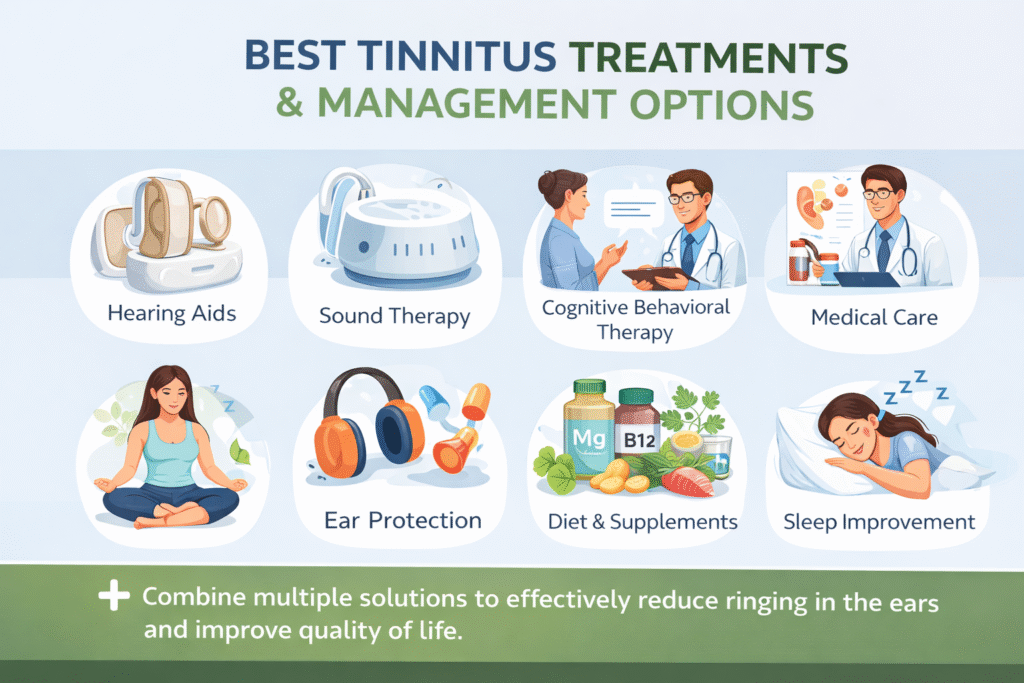
The best tinnitus treatments and management options focus on reducing symptoms, addressing underlying causes, and improving quality of life, since there is no single universal cure for tinnitus. Effective approaches include hearing aids for those with hearing loss, which help restore sound input and reduce the brain’s perception of ringing, as well as sound therapy and white noise devices that mask tinnitus and make it less noticeable, especially at night. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is highly effective for managing the emotional impact of tinnitus, helping reduce anxiety, stress, and sleep problems associated with constant ear noise. Medical treatment may involve managing ear infections, removing earwax, adjusting medications that trigger tinnitus, or treating circulatory and blood pressure issues. Many people also benefit from natural remedies and lifestyle changes, such as reducing caffeine and alcohol, managing stress, improving sleep habits, protecting ears from loud noise, and using supplements like magnesium, vitamin B12, zinc, and ginkgo biloba to support nerve and ear health. When combined in a personalized plan, these treatments can significantly reduce tinnitus intensity, improve daily comfort, and help individuals regain control over their hearing and well-being.
Natural Remedies for Tinnitus Relief
Natural remedies for tinnitus relief focus on improving circulation, reducing inflammation, calming the nervous system, and supporting ear and brain health to lessen the intensity of ringing or buzzing sounds. Many people find relief by using ginkgo biloba, which helps improve blood flow to the inner ear and brain, potentially reducing tinnitus caused by poor circulation, while magnesium and zinc supplements support nerve function and may help decrease auditory sensitivity. Vitamin B12 is also important, as deficiency has been linked to tinnitus in some individuals. Herbal options such as ginger, turmeric, and garlic help reduce inflammation and improve blood flow, while green tea and chamomile tea can calm the nervous system and reduce stress-related tinnitus flare-ups. Lifestyle-based natural remedies are equally important, including stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, and regular exercise, as stress is a major trigger for tinnitus. Reducing caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, and salt intake, staying well hydrated, protecting the ears from loud noise, and ensuring quality sleep can significantly reduce symptom severity. When combined consistently, these natural approaches can help many sufferers experience noticeable improvement in comfort, focus, and overall quality of life.
Tinnitus and Diet: Can Food Help?
Diet can play a meaningful role in managing tinnitus because the foods you eat directly affect inflammation, blood circulation, nerve health, and inner ear function, all of which influence the severity of ringing or buzzing in the ears. A diet rich in leafy greens, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, nuts, seeds, and omega-3 fatty acids supports healthy blood flow to the auditory system and helps protect nerve cells involved in hearing. Foods high in magnesium, zinc, potassium, and vitamin B12—such as bananas, avocados, spinach, eggs, fish, and dairy—may reduce tinnitus intensity, especially in people with nutrient deficiencies. At the same time, limiting caffeine, alcohol, excess salt, sugar, and highly processed foods can prevent fluid imbalance and blood pressure spikes that often worsen tinnitus symptoms. Staying well hydrated and maintaining stable blood sugar levels also helps reduce inner ear stress. While diet alone is not a cure for tinnitus, many sufferers report noticeable improvement when they adopt an anti-inflammatory, nutrient-dense eating plan, making healthy food choices an important part of a comprehensive tinnitus management strategy.
Why Tinnitus Should Not Be Ignored
Tinnitus should never be ignored because it is often a warning sign that something is wrong within the auditory system or elsewhere in the body, such as hearing loss, nerve damage, ear infections, circulatory disorders, high blood pressure, TMJ problems, or even neurological conditions. While many people dismiss ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the ears as a minor annoyance, persistent tinnitus can gradually worsen and lead to serious consequences, including chronic stress, anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, difficulty concentrating, and reduced quality of life. In some cases, tinnitus may indicate more serious health issues like Meniere’s disease, acoustic neuroma, or vascular abnormalities, especially if it appears suddenly, affects only one ear, or is accompanied by dizziness, balance problems, or hearing loss. Early medical evaluation can help identify the underlying cause, prevent further damage, and allow for timely treatment or management. Ignoring tinnitus not only increases the risk of long-term complications but can also make the condition harder to manage over time, which is why taking symptoms seriously and seeking professional advice is essential for protecting both hearing and overall health.
When to See a Doctor
You should see a doctor as soon as possible if tinnitus is persistent, worsening, or interfering with your daily life, sleep, concentration, or emotional well-being, as early evaluation greatly improves outcomes. Immediate medical attention is especially important if tinnitus appears suddenly, occurs in only one ear, is accompanied by hearing loss, dizziness, vertigo, balance problems, ear pain, ear discharge, headaches, or facial weakness, or if you hear a pulsing sound in sync with your heartbeat, which may indicate a circulatory or neurological issue. Tinnitus following head injury, loud noise exposure, or infection should also be assessed promptly to prevent permanent damage. Additionally, if tinnitus is linked to new medications, a doctor can determine whether drug side effects are involved and adjust treatment accordingly. Because tinnitus can be a symptom of conditions such as inner ear disorders, high blood pressure, nerve damage, Meniere’s disease, or acoustic neuroma, seeking professional evaluation ensures serious causes are ruled out and appropriate treatment or management begins early, helping to protect your hearing, reduce complications, and improve quality of life.
Conclusion: Take Control of Tinnitus Today
Tinnitus can be frustrating, but you are not powerless. With the right combination of tinnitus treatment, natural remedies, lifestyle changes, and nutritional support, many people experience noticeable relief. Whether you are searching for how to stop ringing in the ears, the best tinnitus supplements, or natural tinnitus relief, the key is to act early and support your hearing health holistically.

